3.3 PASS:
Rotation of a straight interface
-
Author
- Stéphane Popinet
- Command
- gerris2D rotate.gfs
- Version
- 110920
- Required files
- rotate.gfs (view) (download)
rotate.gfv cells.gfv error.ref n1-0.gnu n1-1.gnu n1-2.gnu n1-5.gnu error.n1
- Running time
-
A straight interface is advected by a pure shear flow. The exact
solution is simply a rotation of the interface around the center of
the box. Note that both the interface and the velocity field should
be described exactly by a second-order method.
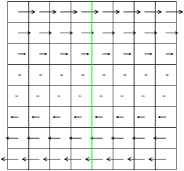
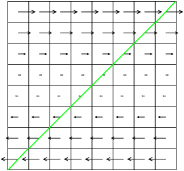
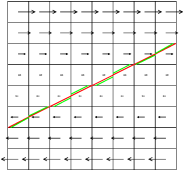
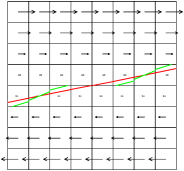
Figure 41 illustrates what happens when using a VOF
scheme to follow the interface. The green segments are the
VOF-reconstructed interface obtained when using a "naive" Eulerian
PLIC method. The red segments are the VOF-reconstructed interface
obtained when using a "multiband" Eulerian PLIC method (with n = 4
bands).
Figure 42 illustrates the evolution of the error with
time. For t=1 the interface is at 45 degrees and the errors in
fluxes cancel out exactly.
| Figure 41: Evolution of the VOF interface (green n =
1, red n = 4) in a shear flow. (a) t=0, (b) t=1, (c) t=2,
(d) t=5. |
| Figure 42: Volume fraction error as a function of time. |