 |



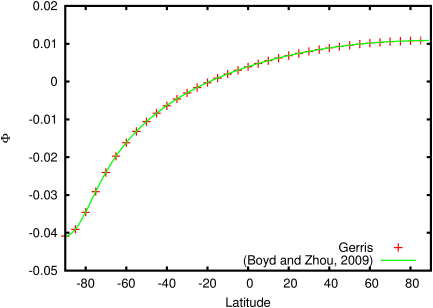
This test case is inspired from [9] who derived an analytical solution for the Poisson equation on a sphere forced by a Gaussian term on the north pole. The equation is of the form
| ∇2 Φ = exp(−2 є2 (1−cos(θ+ |
| ))) − cste |
The problem is axisymmetric and has for solution:
| Φ = |
| ⎛ ⎝ | 1 − exp(−4 є2) | ⎞ ⎠ | log(1−x) − |
| exp(−4 є2) log | ⎛ ⎜ ⎜ ⎝ |
| ⎞ ⎟ ⎟ ⎠ |
| + |
| E1 (2 є2 (1−x)) + |
| exp(−4 є2) Ei(2 є2 (1+x)) |
where E1 is the exponential integral function, Ei(x) = −Re (E1(−x)) and x = cos(θ+π/2).
The solution is not easy to compute and was evaluated over a cross-section using the Maxima software.
Same test case but using a longitude-latitude metric. The errors are larger near the poles and the convergence rate of the multigrid solver much lower due to the large scale ratio between cells at the poles and at the equator.


